FAFDrugs4




For some of them, according to reports in the literature and a structural analysis of approved drugs, we decided to apply a threshold cutoff on the number of occurrences of a given substructure in the same compound.
For instance we accept up to 3 nitro groups (although nitro are well-known structural alerts) because several approved drugs have a nitro group and because this group can be replaced during optimization (72).
Depending on such analysis, the molecule is then categorized in three baskets or to the PAINS basket:
• Accepted
Compounds with no structural alerts and satisfying the physicochemical filter.
• Intermediate
Compounds which embeds low-risk structural alerts with a number of occurrences below the threshold.
(the notion of low risk structural alerts has to be considered within the context of the project, the type of diseases...).
• Rejected
Compounds that do not pass the selected or user defined physicochemical filter.
Compounds that that include a high-risk structural alert and/or exceed the threshold of occurrence of low-risk structural alerts.
• PAINS
Compounds flagged due to the presence of some chemical groups that belong to the PAINS category.
| Substructure | 2D Depiction | Rejection Threshold | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1_2_aminothiazole |
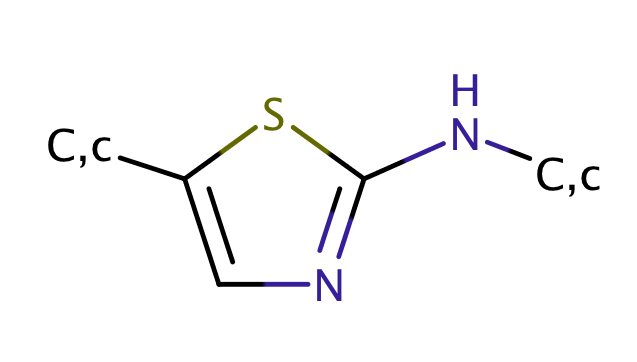
|
1 | 44 |
| 1_2_dicarbonyl_oxalyl |
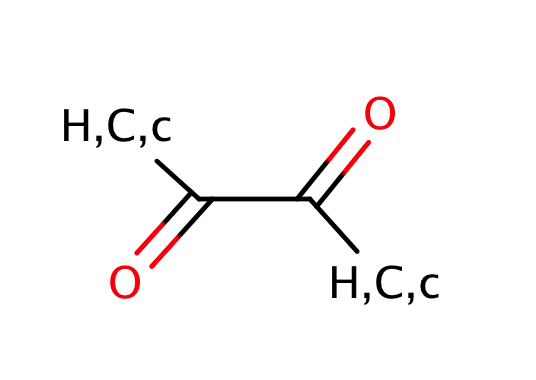
|
0 | 55, 56, 58 |
| 1_2_thiazol_3_one |
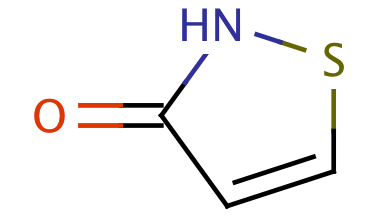
|
1 | 63 |
| 1_aminobenzotriazole |
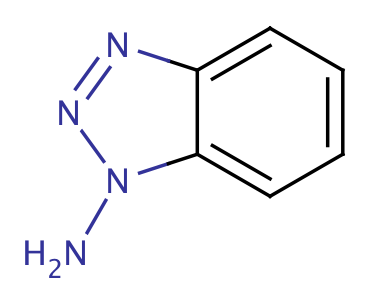
|
1 | 65 |
| 2_phenylbenzimidazole |
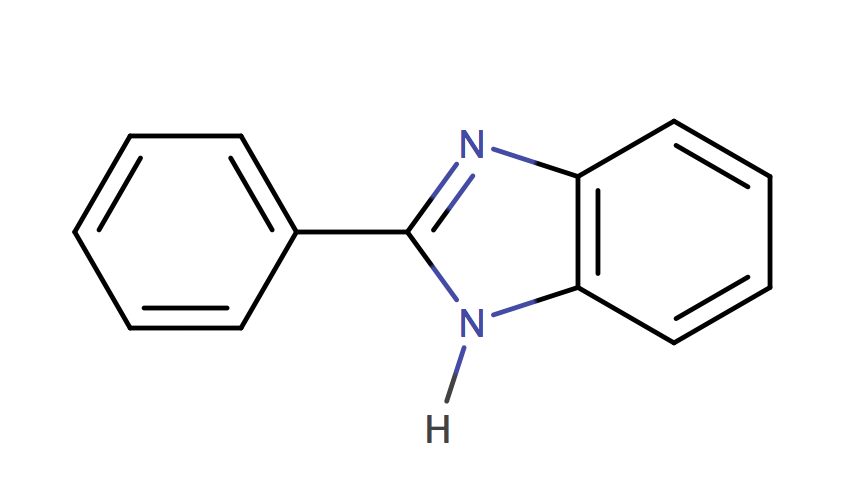
|
1 | 44, 6 |
| 3_amino_9_ethylcarbazoles |
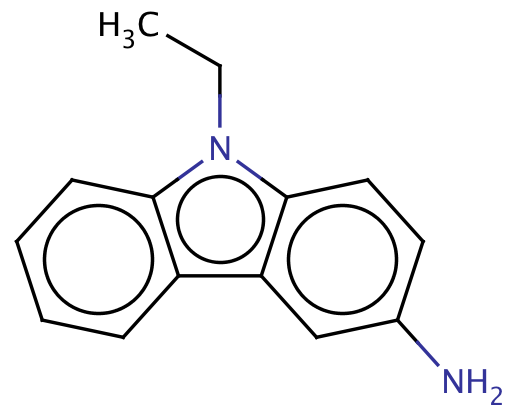
|
1 | 66 |
| 4_subst_n_alkyltetrahydropyridines |
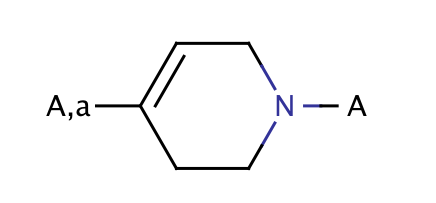
|
1 | 44 |
| 4_vinyl_pyridine |
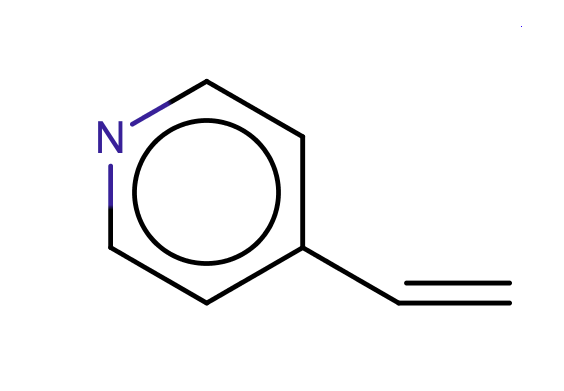
|
no limit | 61 |
| 6_membered_aromatic_sulfur_NSN |
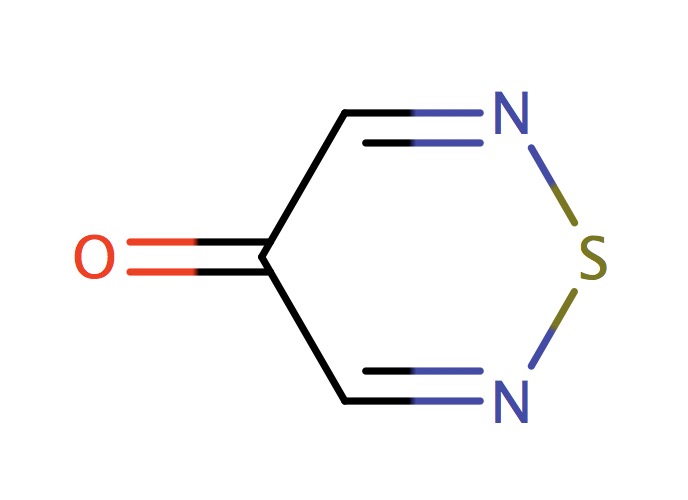
|
0 | 73 |
| 6_membered_aromatic_sulfur_NSC |
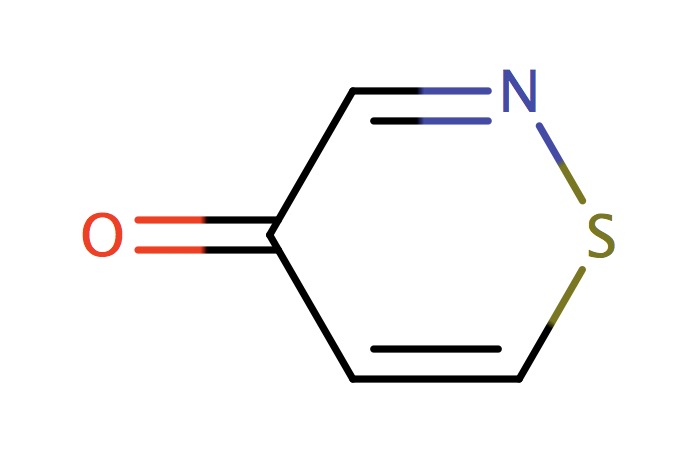
|
1 | 73 |
| 6_membered_aromatic_sulfur_CSN |
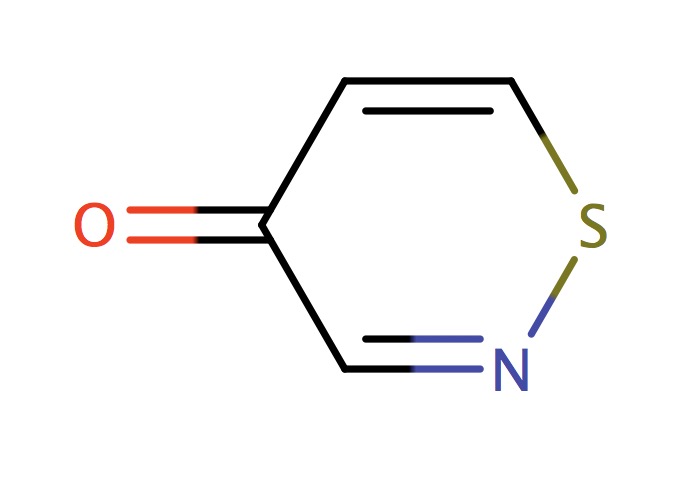
|
1 | 73 |
| 6_membered_aromatic_sulfur_CSC |
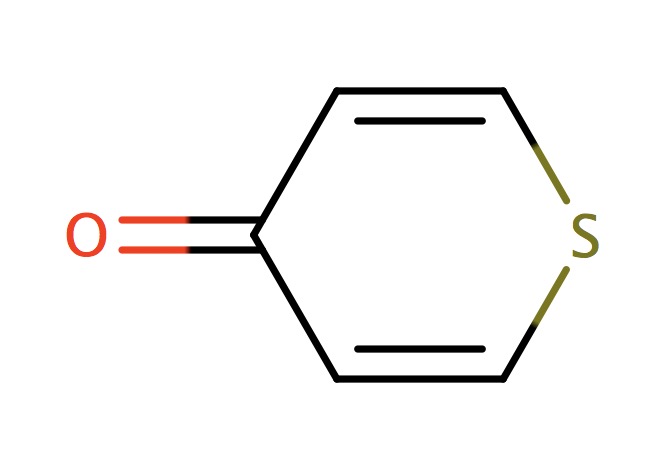
|
1 | 73 |
| 9_aminoacridine |
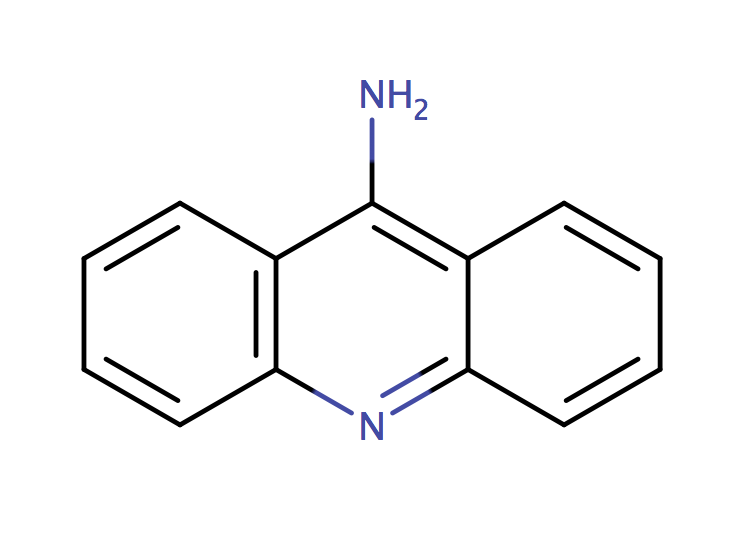
|
1 | 44, 6 |
| acetal_1_in_ring |
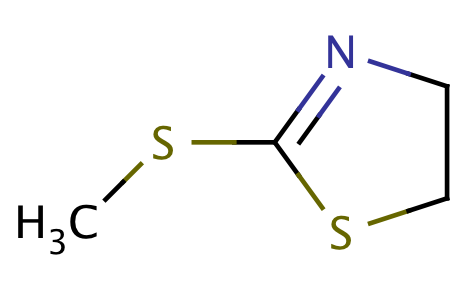
|
1 | 53 |
| acetal_both_in_ring |
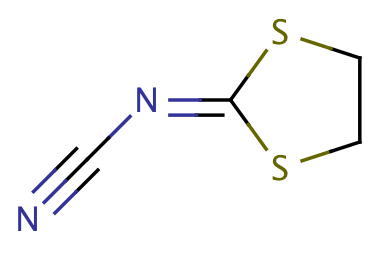
|
1 | 53 |
| acetylene_alkyne |
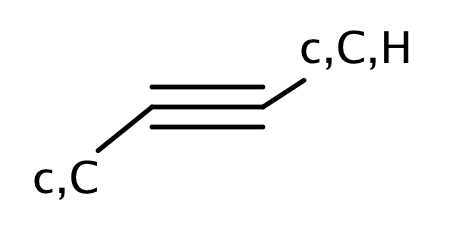
|
1 | 44, 58 |
| acrylamide |
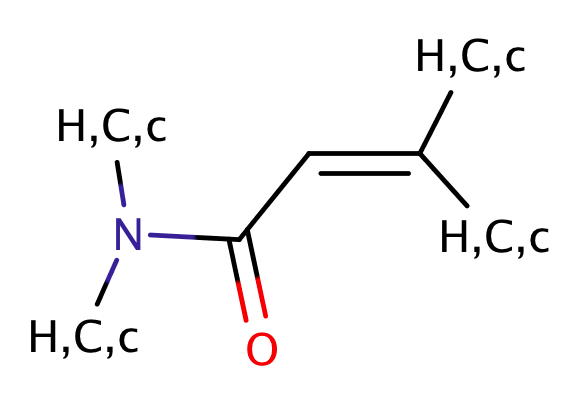
|
1 | 23, 56 |
| acyclic_acetal |
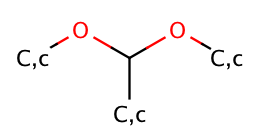
|
no limit | 67 |
| acyclic_acid_halide_acyl_halide |
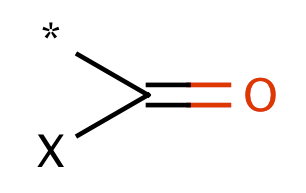
|
0 | 55 |
| acyl_amide |
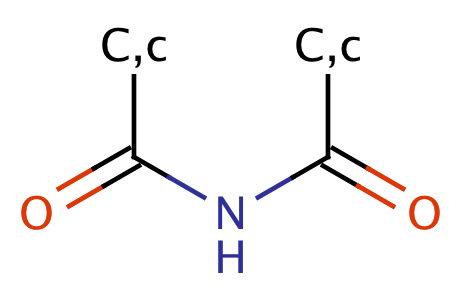
|
1 | 56, 58, 59 |
| acyl_cyanides |
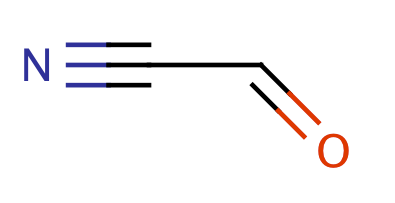
|
0 | 31 |
| acyl_isoamide_aromatic |
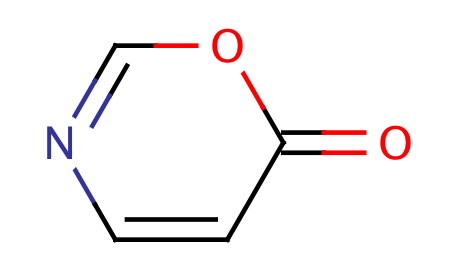
|
1 | 53 |
| adamantane |
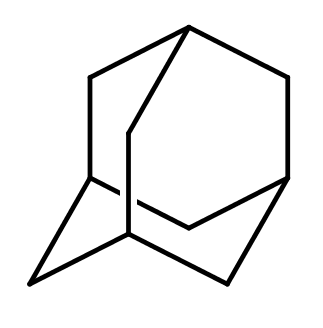
|
1 | 53 |
| aldehyde |
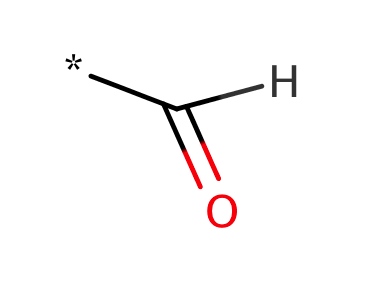
|
0 | 53, 55, 58, 60, 61 |
| aliphatic_ketone |
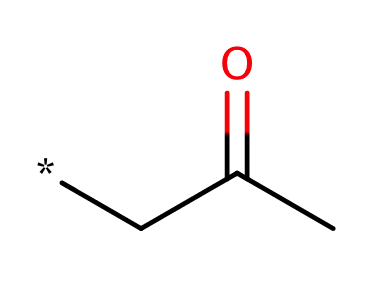
|
0 | 18, 44 |
| alkyl_halide_I |
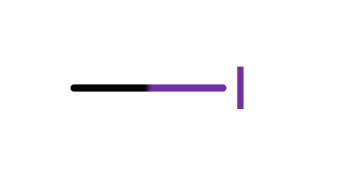
|
1 | 56 |
| alkyl_halide_Cl_Br |
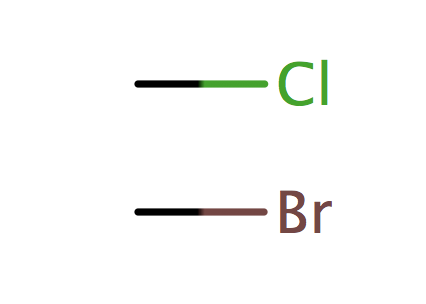
|
1 | 56 |
| alphahalo_ketone_carbonyl |
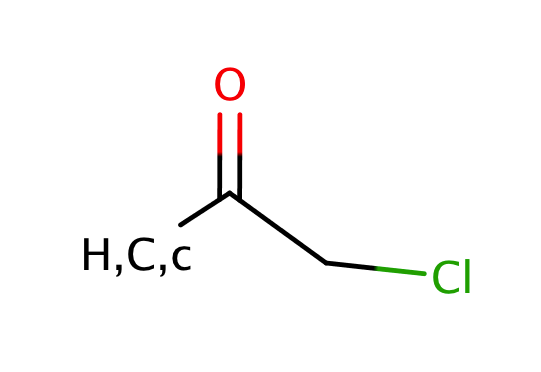
|
0 | 55 |
| anhydride |
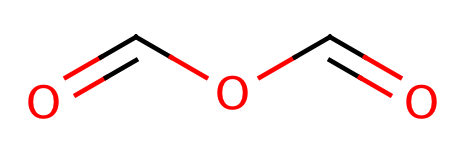
|
0 | 55 |
| anthracene |
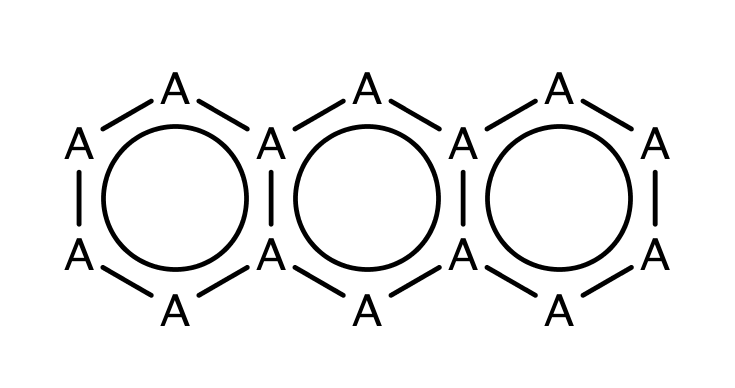
|
1 | 23, 55, 63 |
| azide |
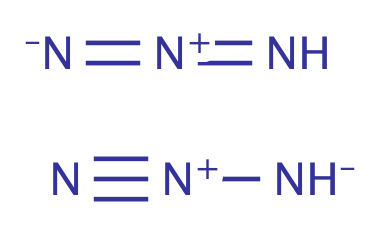
|
1 | 31, 55, 60 |
| aziridine |
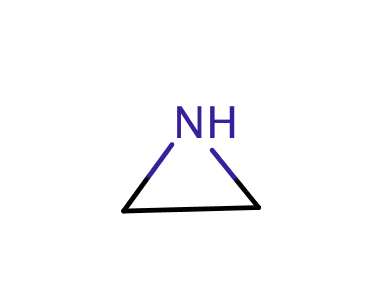
|
0 | 18, 55, 60, 62 |
| azo |
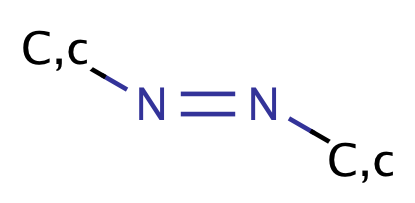
|
1 | 60, 63 |
| azocyanamide |
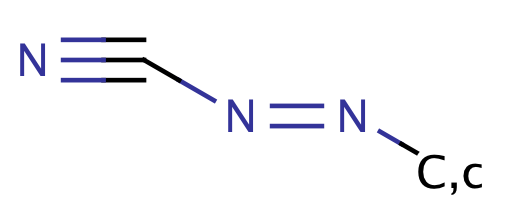
|
1 | 64 |
| beta_heterosubstituted_carbonyl |
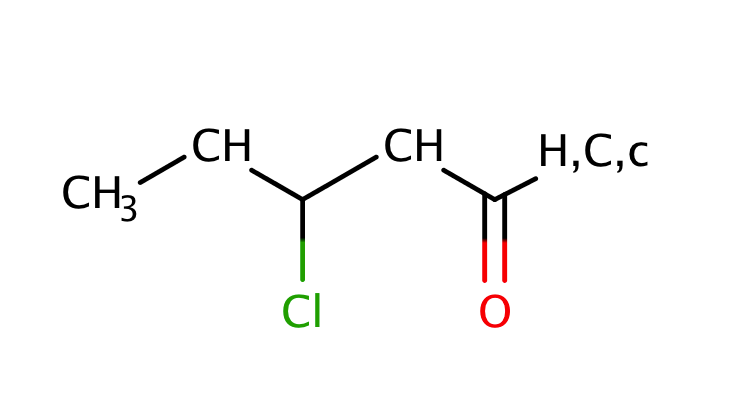
|
1 | 55, 56 |
| betalactams |
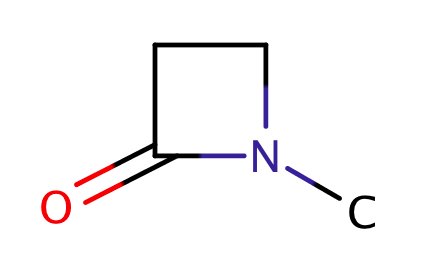
|
1 | 18 |
| carbamic_acid |
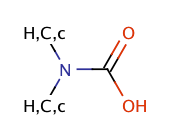
|
no limit | 23 |
| carbazide |
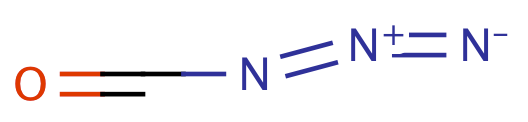
|
0 | 64 |
| carbodiimide |
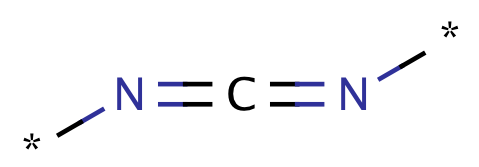
|
1 | 55, 63 |
| catechol |
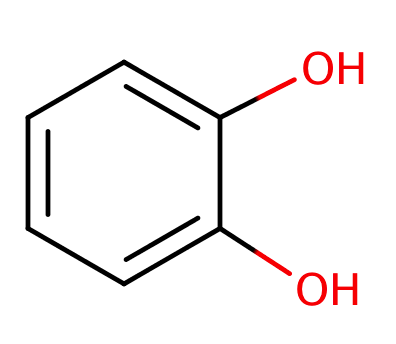
|
1 | 58, 6 |
| chloramidine |
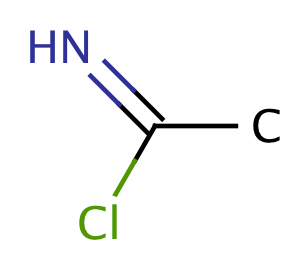
|
1 | 64 |
| consecutive_alkyl_chains |
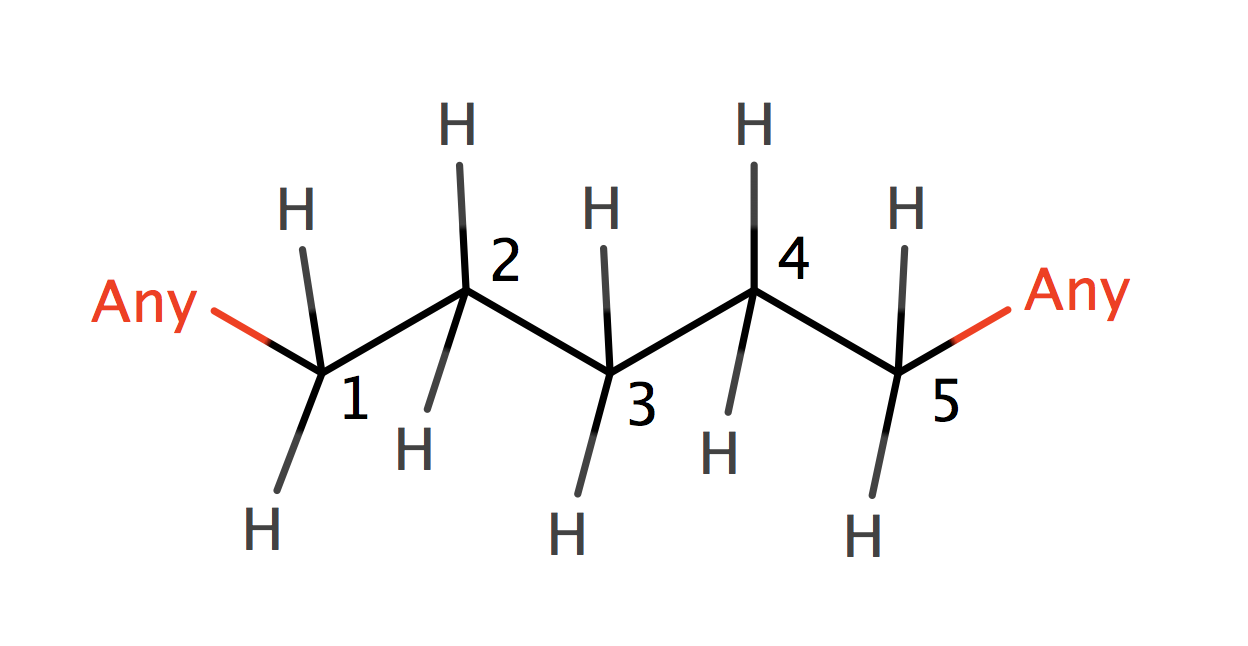
|
0 | 44, 6 |
| coumarines |
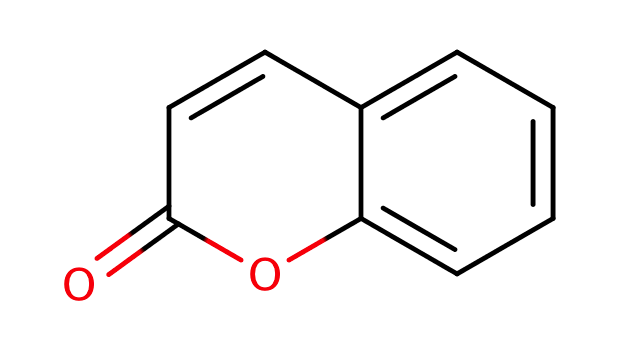
|
1 | 44, 6 |
| cyanohydrins |
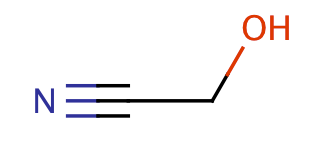
|
0 | 63 |
| cyanophosphonate |
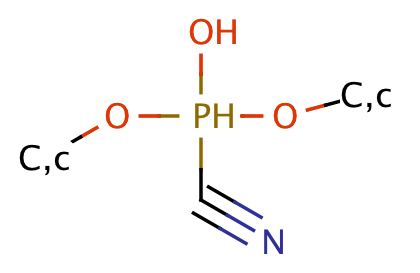
|
1 | 64 |
| cyclic_crown_2_2 |
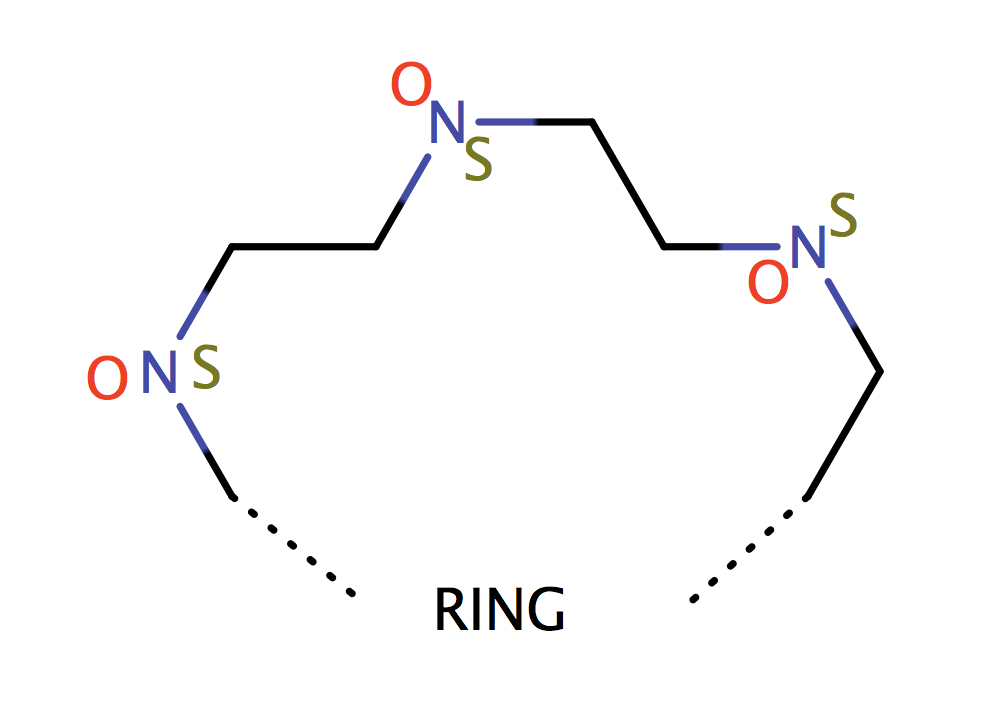
|
1 | 31, 53, 60 |
| cyclic_crown_2_3 |
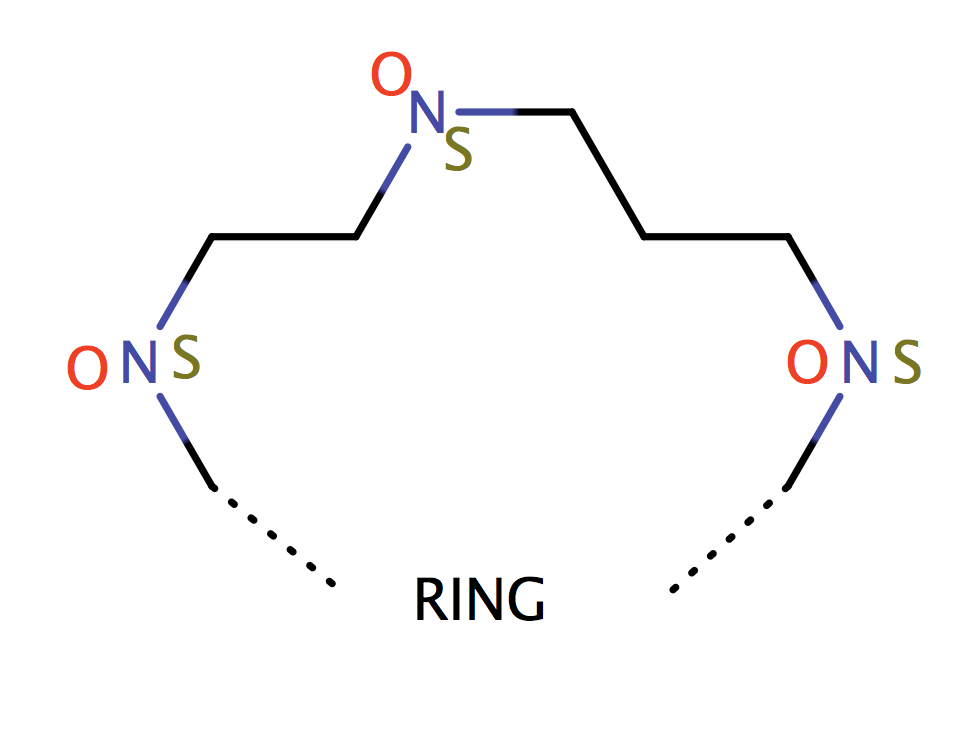
|
1 | 53 |
| cyclic_crown_3_3 |
|
1 | 53 |
| diazonium |
|
1 | 31, 56, 57, 63 |
| ellipticine |
|
1 | 44, 6 |
| enamine |
|
no limit | 23, 53 |
| epoxide |
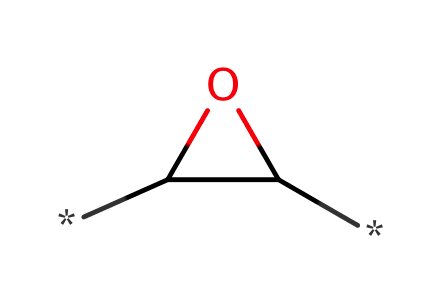
|
0 | 18, 56, 58 |
| fmoc |
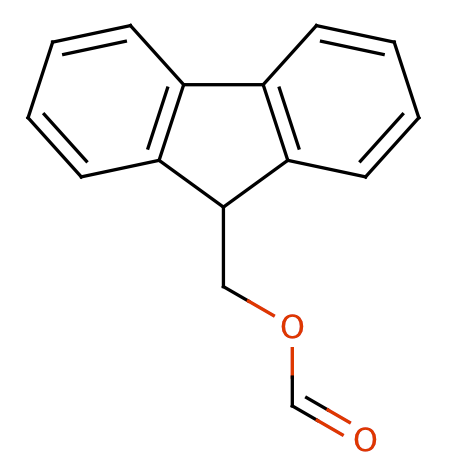
|
1 | 53 |
| formic_acid_esters |
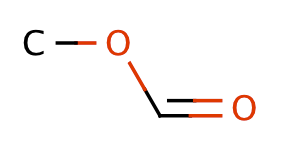
|
1 | 63 |
| furocoumarines |
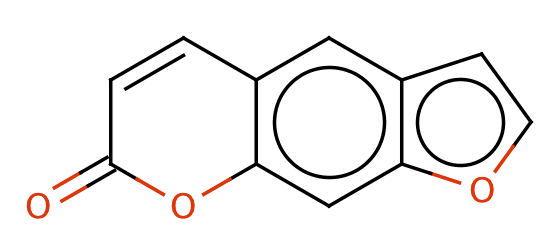
|
1 | 44, 6 |
| halo_alkene |
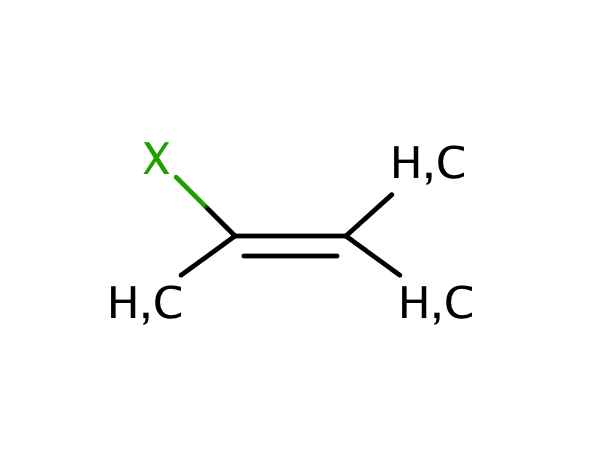
|
no limit | 60, 55 |
| halo_amine |
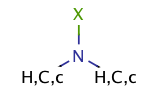
|
no limit | 68 |
| halogenure |
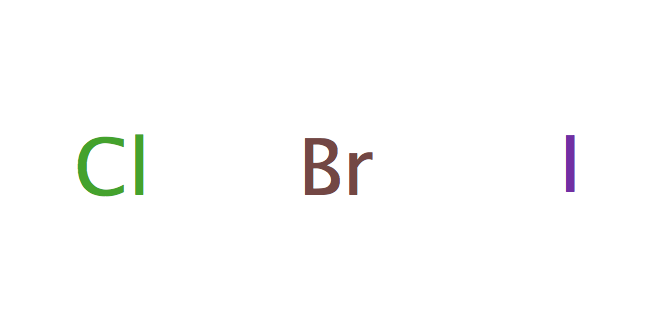
|
5 | |
| halogenure_F |

|
7 | |
| halopyrimidine |
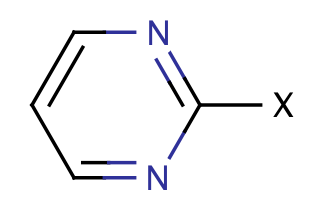
|
0 | 18 |
| hemiaminal |
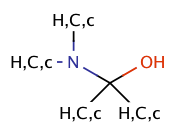
|
no limit | 23, 53 |
| hemiketal |
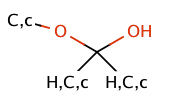
|
no limit | 64 |
| heteroatom_heteroatom_N_N |
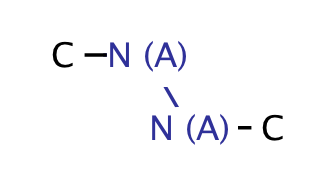
|
0 | 18 |
| heteroatom_heteroatom_N_S |
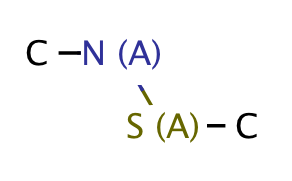
|
0 | 18 |
| heteroatom_heteroatom_O_N |
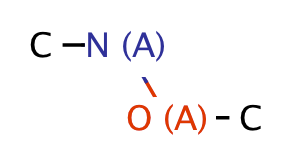
|
0 | 18 |
| heteroatom_heteroatom_S_O |
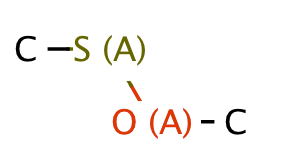
|
0 | 18 |
| heteroatom_heteroatom_S_S |
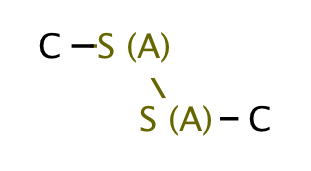
|
0 | 18 |
| hydantoin |
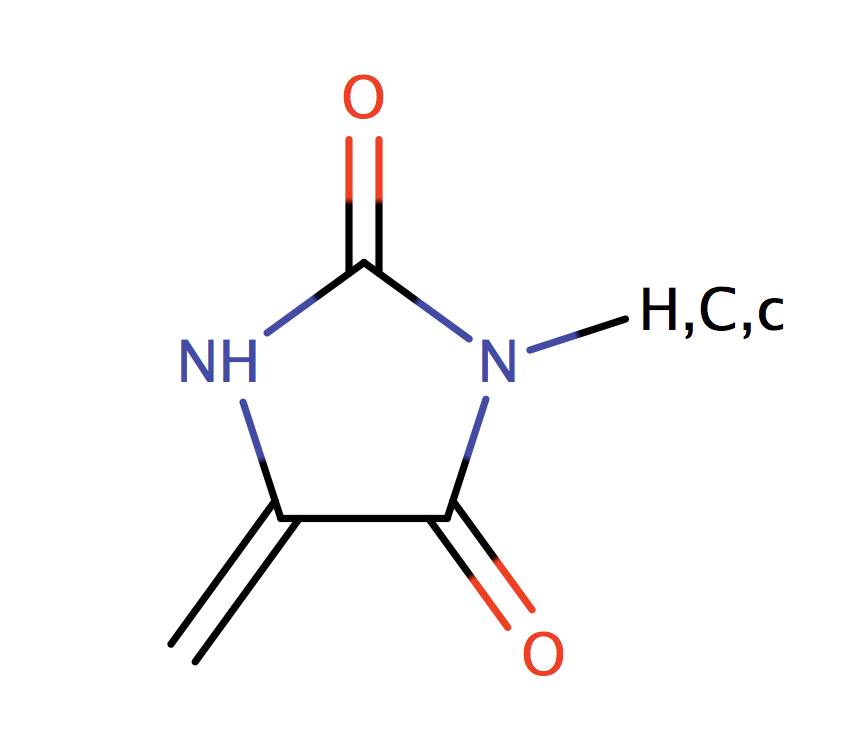
|
1 | 44 |
| hydralazine |
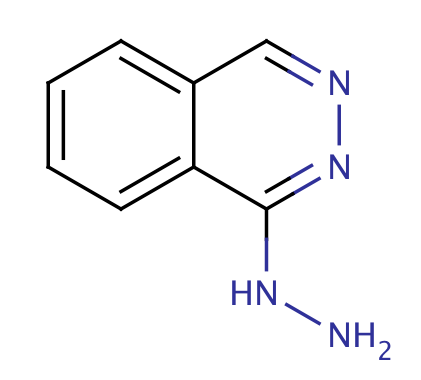
|
1 | 44 |
| hydrazide |
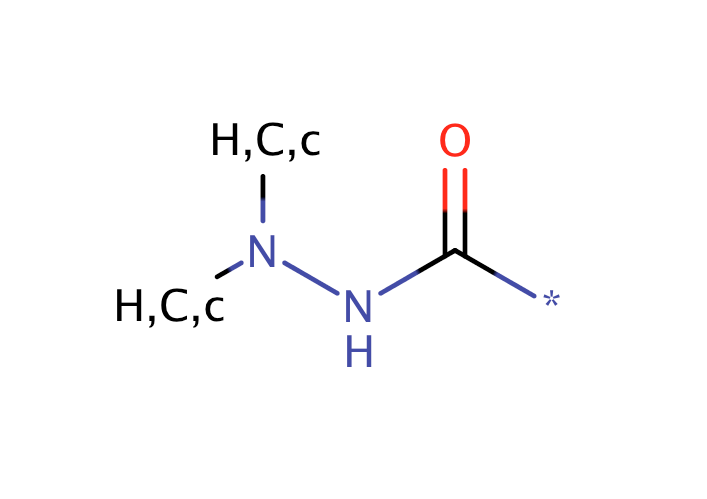
|
1 | 56, 57 |
| hydrazine |
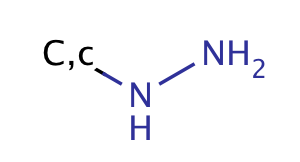
|
no limit | 56, 57 |
| hydrazone |
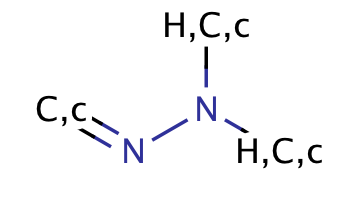
|
no limit | 56, 57 |
| hydroxamic_acid |
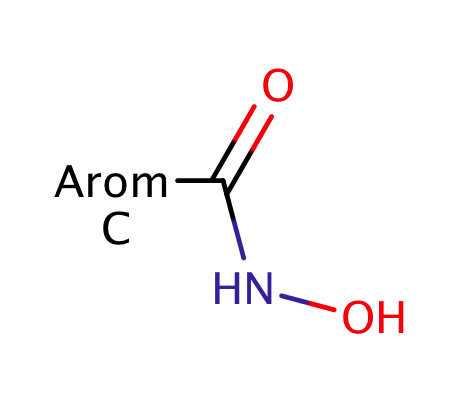
|
no limit | 44 |
| hydroxylamine |
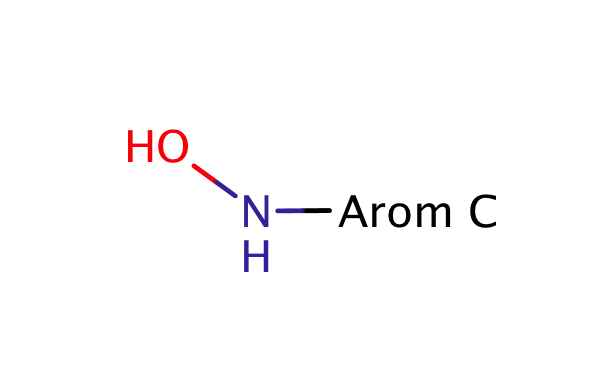
|
no limit | 44, 56 |
| imidazole |
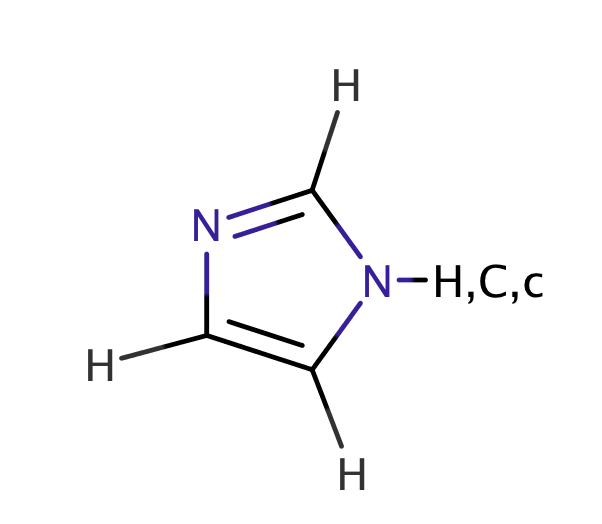
|
1 | 44 |
| imide |
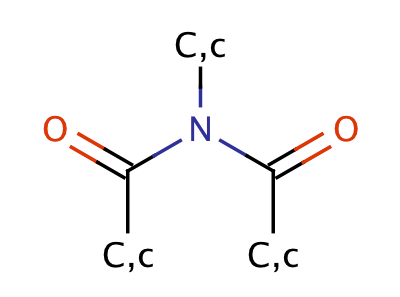
|
1 | 56, 57 |
| imidoyl_halide |
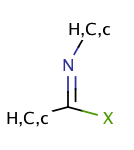
|
no limit | 55 |
| imine_C |
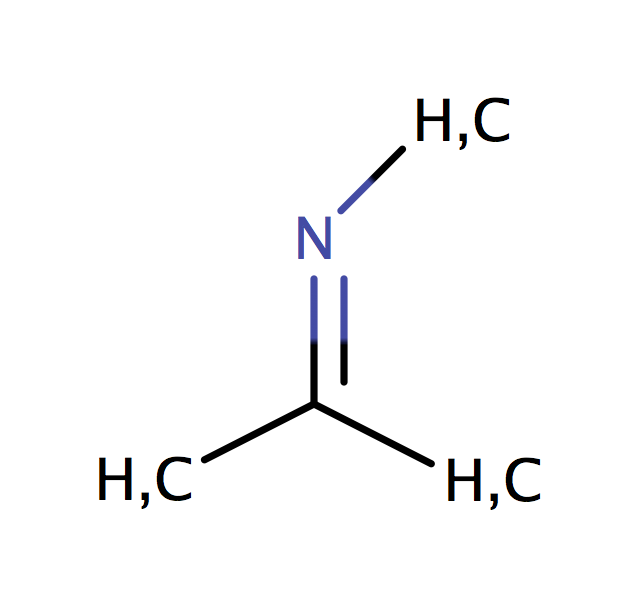
|
0 | 44 |
| imine_c_arom |
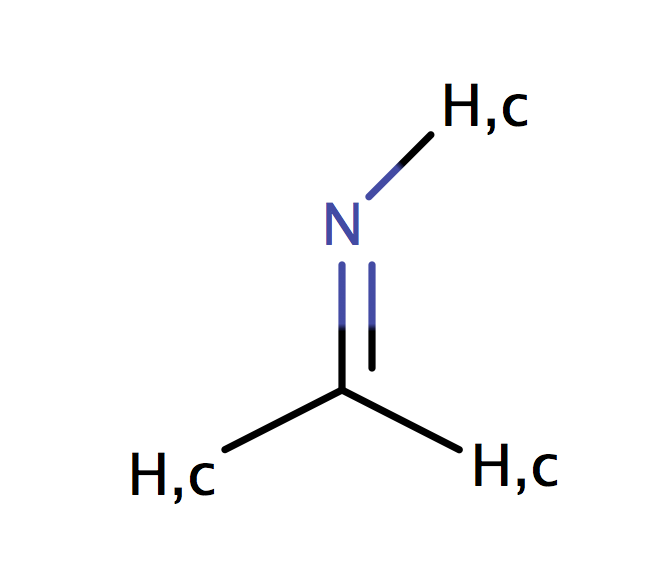
|
no limit | 44 |
| isocyanate |
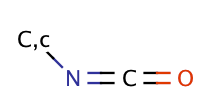
|
no limit | 60 |
| isocyanide_isonitrile |
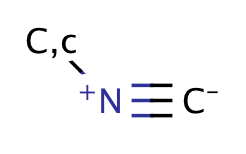
|
no limit | 44 |
| isothiocyanate |
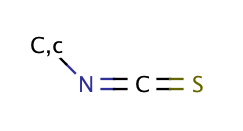
|
0 | 60 |
| lawesson_reagent_derivative |
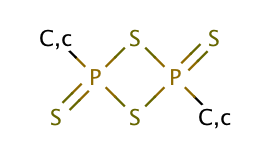
|
1 | 64 |
| maleimide |
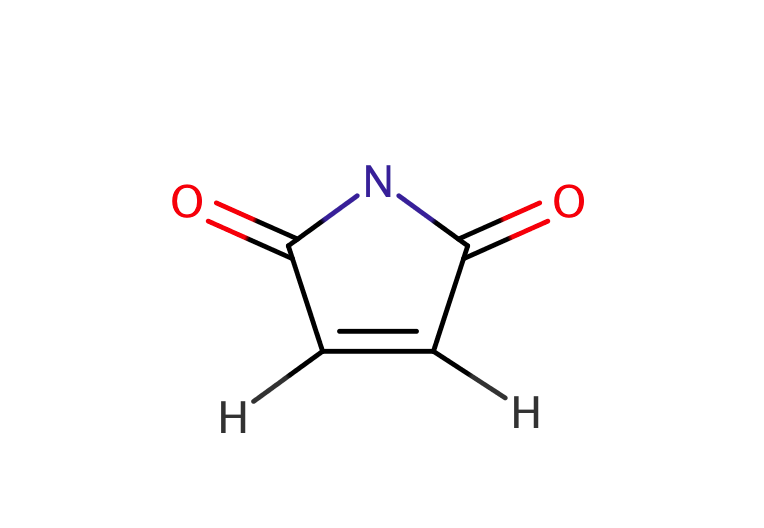
|
no limit | 23, 53 |
| meta_aminophenol |
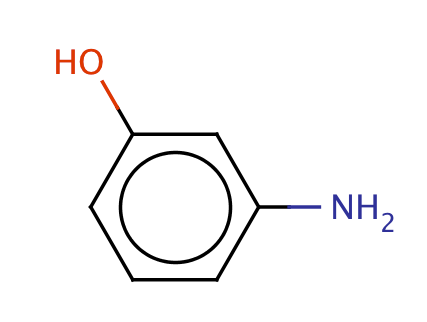
|
0 | 55, 56, 58, 61 |
| michael_acceptors |
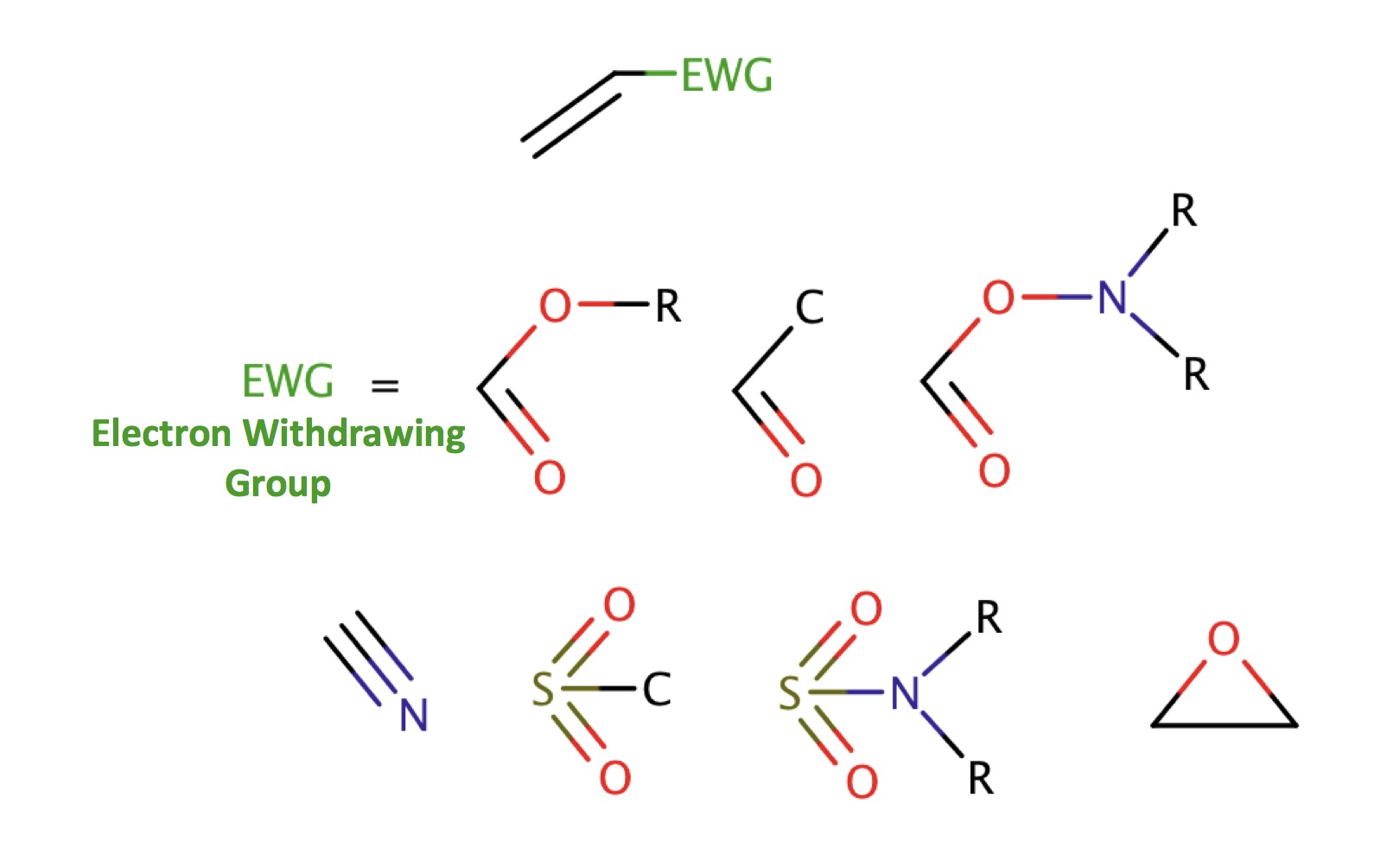
|
0 | 18, 44, 53, 63, 64 |
| mustard_gas |
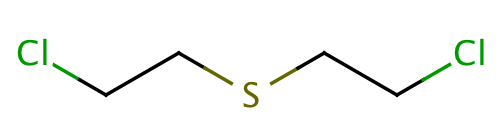
|
1 | 66 |
| nitramine |
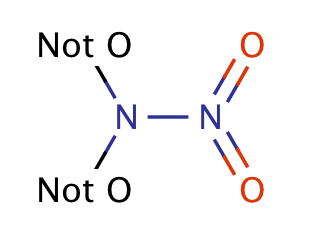
|
1 | 63 |
| nitro |
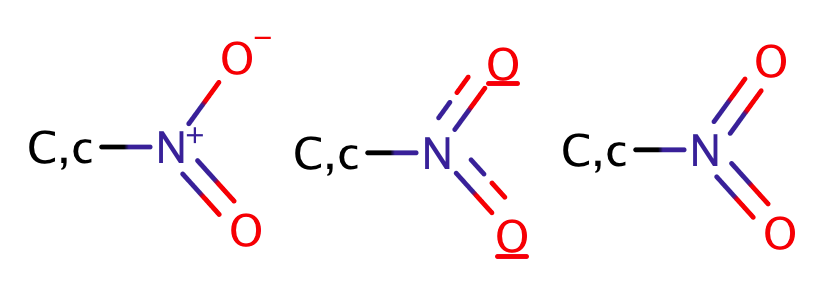
|
3 | 55, 58, 60, 61 |
| nitroso |
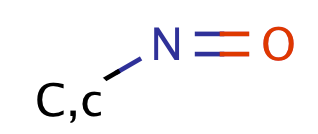
|
no limit | 60 |
| ortho_aminophenol |
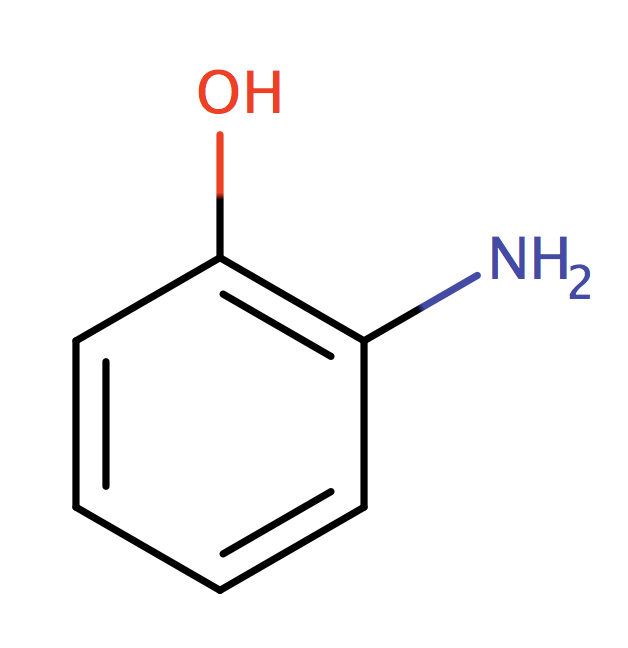
|
0 | 55, 56, 58, 61 |
| ortho_aniline |
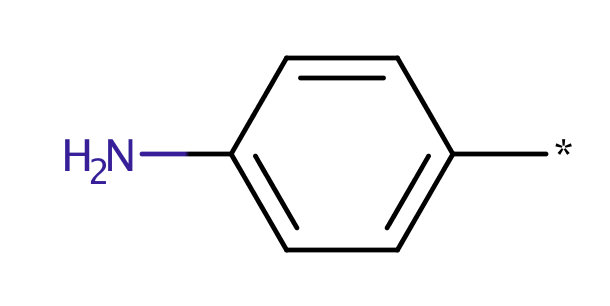
|
0 | 44 |
| ortho_hydroxyanilines |
|
1 | 44 |
| orthonitrophenyl_ester |
|
1 | 66 |
| orthoquinone |
|
0 | 44 |
| oxime |
|
1 | 56, 57 |
| oxonium |
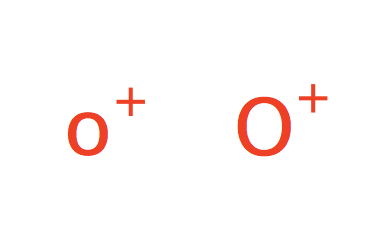
|
no limit | 31 |
| para_aminophenol |
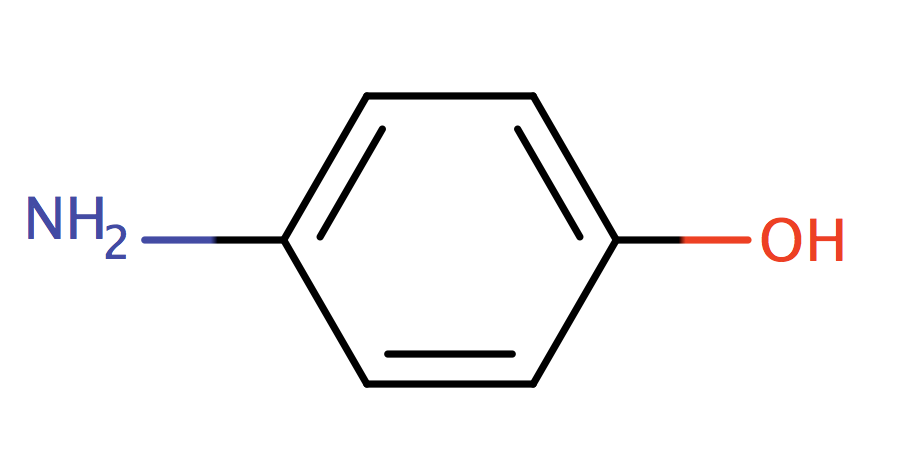
|
0 | 55, 56, 58, 61 |
| para_hydroquinone |
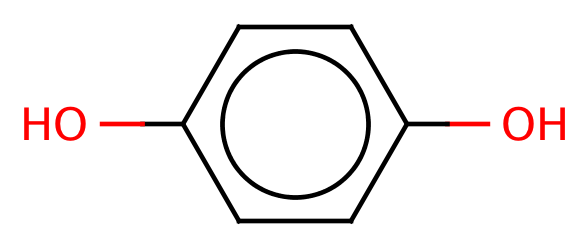
|
0 | 44 |
| para_hydroxyanilines |
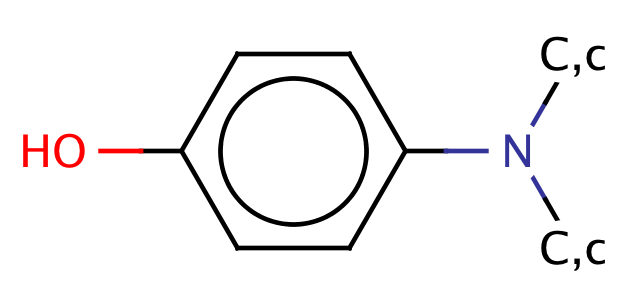
|
1 | 44 |
| para_para_dihydroxybiphenyl |
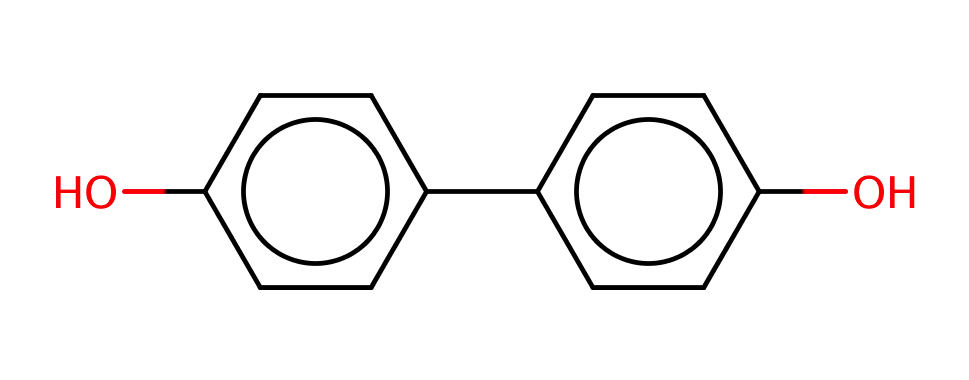
|
1 | 63 |
| para_para_dihydroxystilbene |
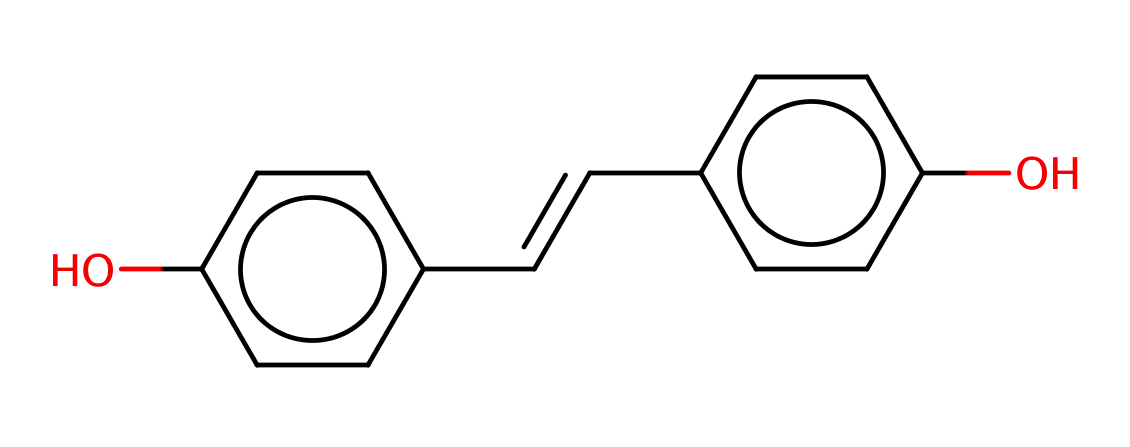
|
1 | 63 |
| paranitrophenyl_ester |
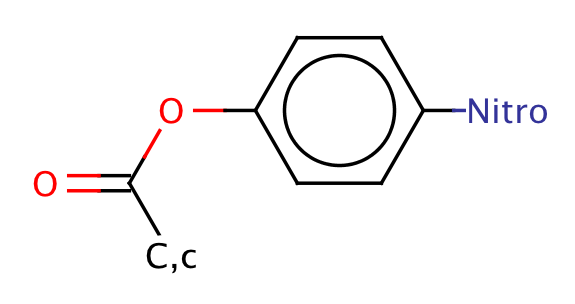
|
1 | 64 |
| pentafluorophen_ester |
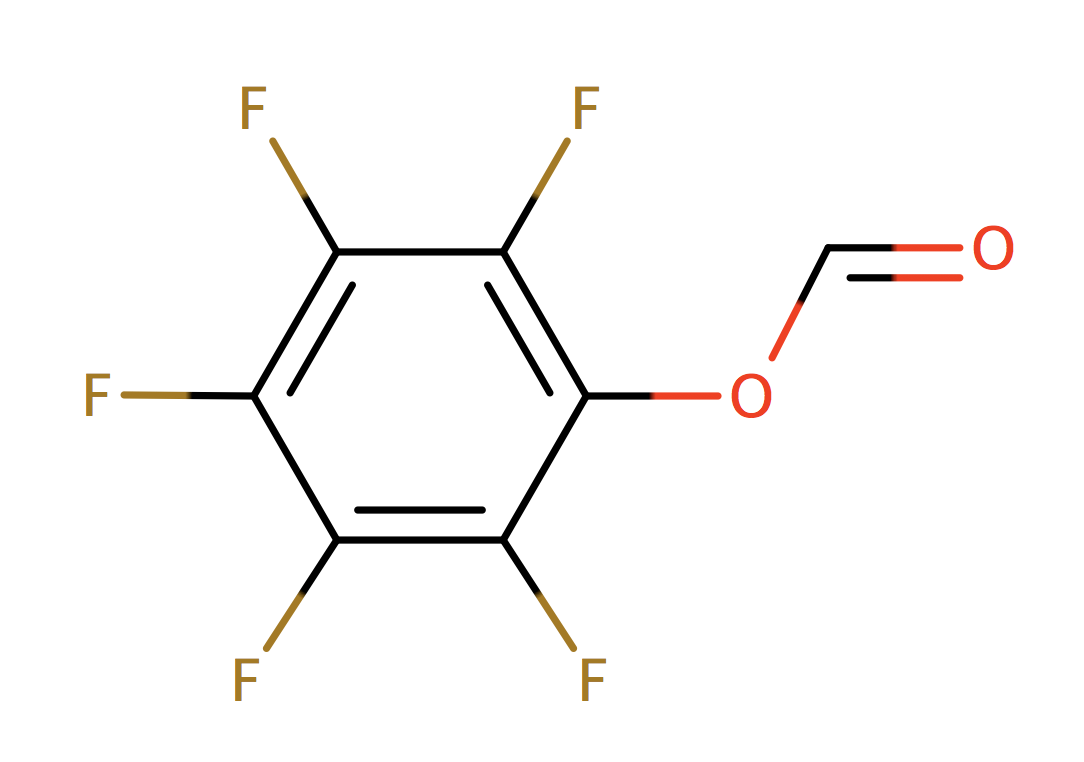
|
1 | 64 |
| perhaloketone |
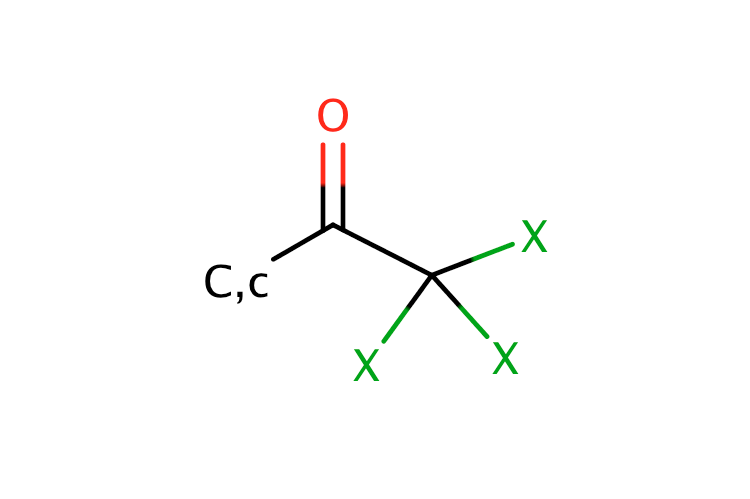
|
0 | 18 |
| peroxide |
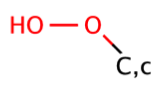
|
0 | 31, 44, 60 |
| phenanthrene_het_N_C |
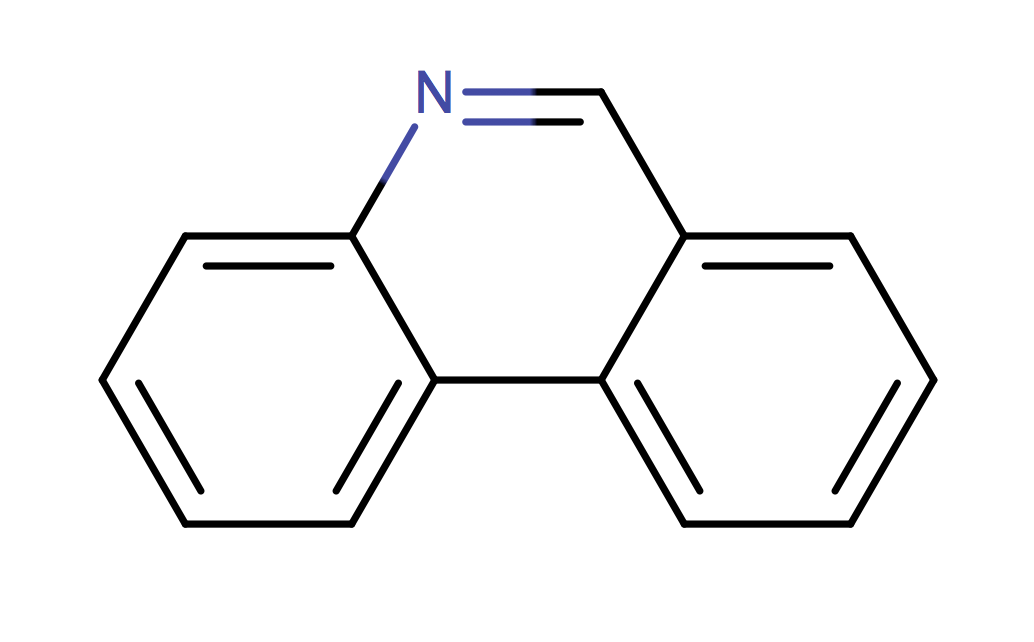
|
1 | 53 |
| phenanthrene_het_C_N |
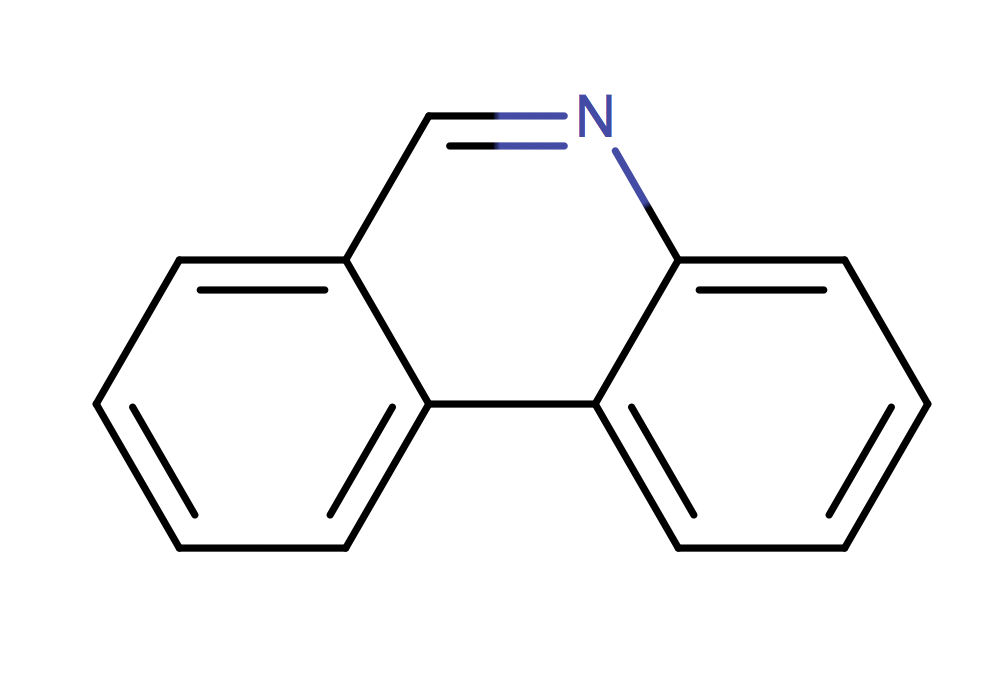
|
1 | 53 |
| phenanthrene_het_N_N |
|
1 | 53 |
| phenol |
|
5 | 31, 44, 60 |
| phosphorane |
|
1 | 44 |
| phosphonic_acid |
|
6 | 53 |
| polyenes |
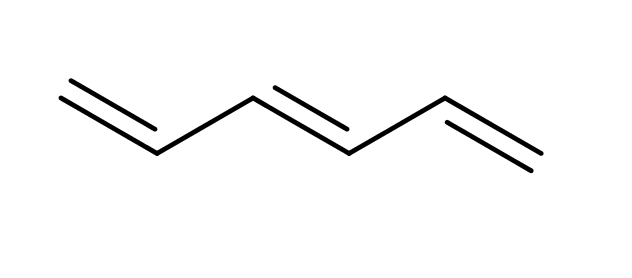
|
no limit | 31 |
| propiolactone |
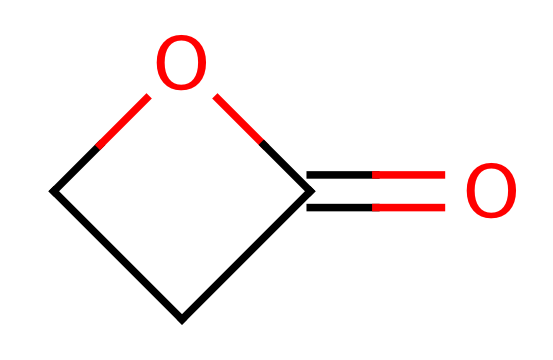
|
1 | 44, 6 |
| propiosultone |
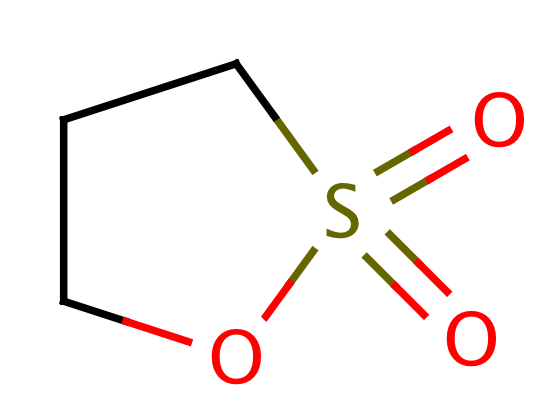
|
1 | 44, 6 |
| quinone |
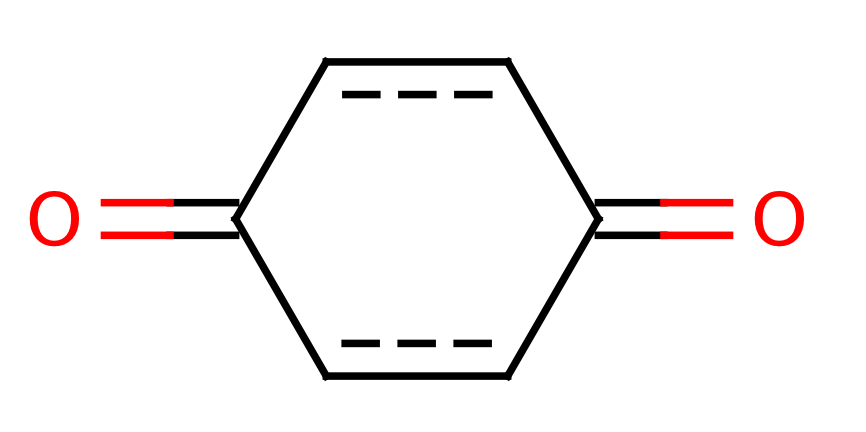
|
0 | 44 |
| sulfonate_ester |
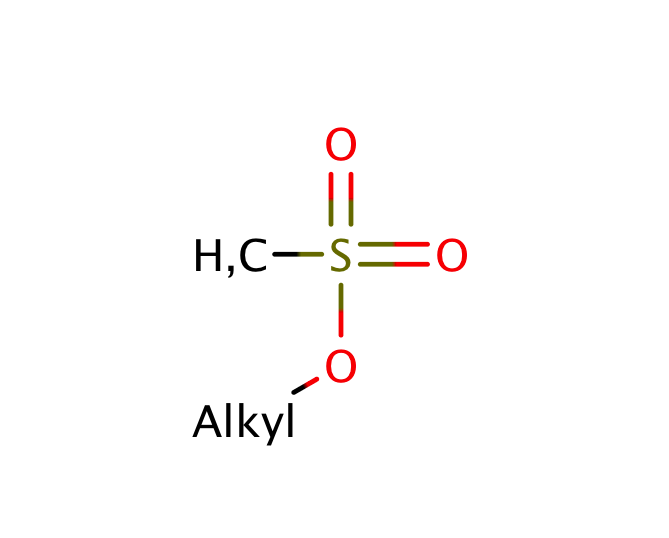
|
0 | 44, 55 |
| sulfonic_acid |
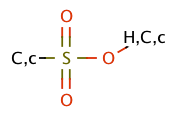
|
no limit | 44, 55 |
| sulfonic_acid_ester |
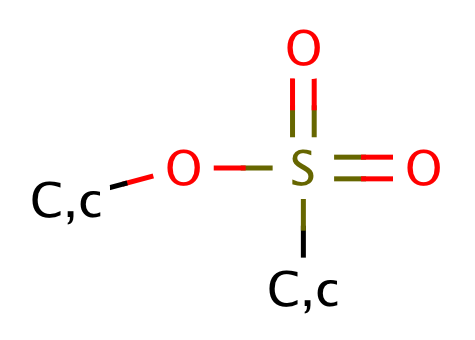
|
1 | 44, 55 |
| sulfonium |
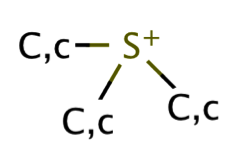
|
1 | 31, 53, 66 |
| sulfonyl_cyanide |
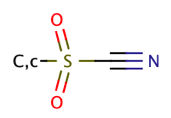
|
0 | 55 |
| sulfonyl_halide |
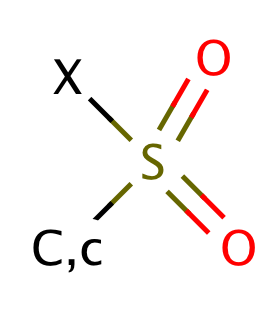
|
0 | 55 |
| sulfonyl_urea |
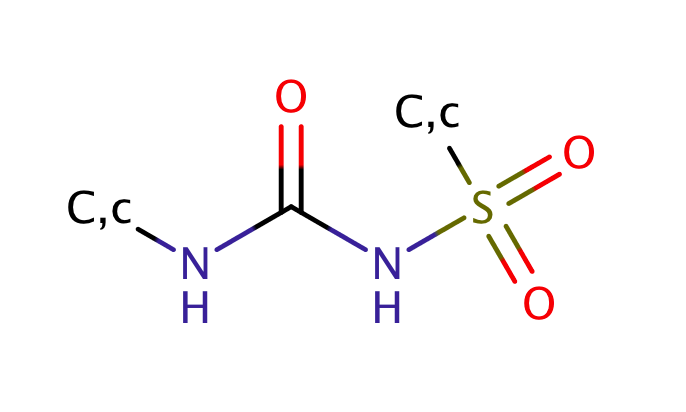
|
1 | 56 |
| sulfoxide |
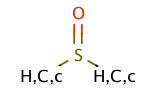
|
no limit | 44, 6 |
| sulphanylamino |
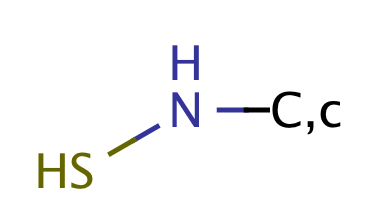
|
1 | 64 |
| thiazolidinedione |
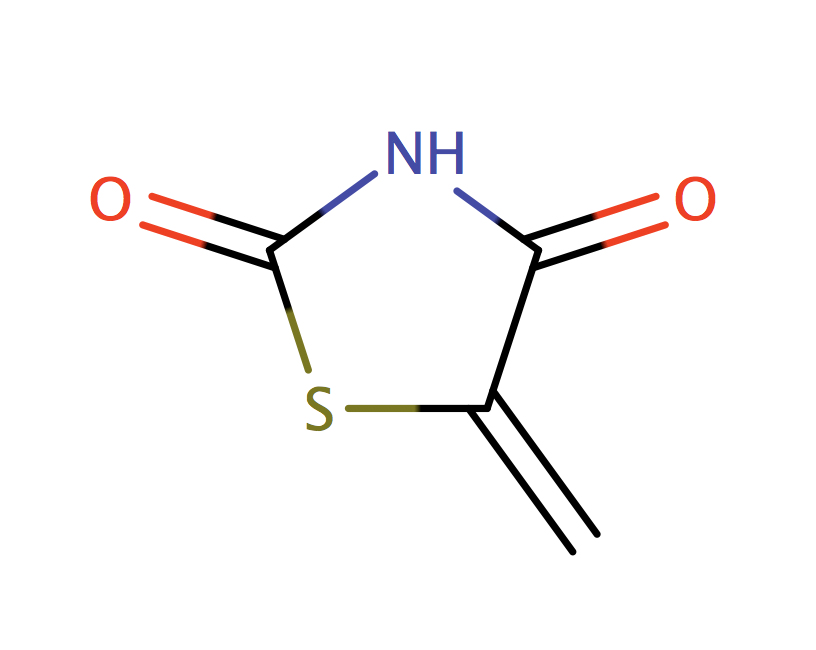
|
1 | 44 |
| thioacetal |
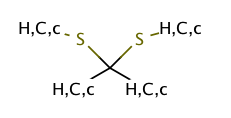
|
no limit | 44 |
| thiocarbamate |
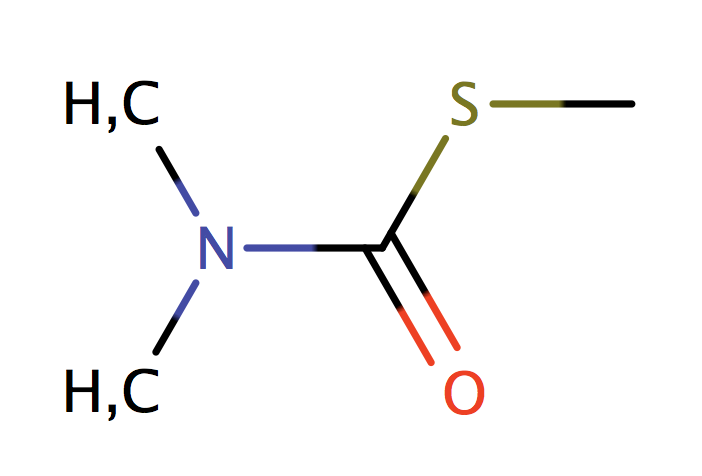
|
no limit | 44 |
| thioester |
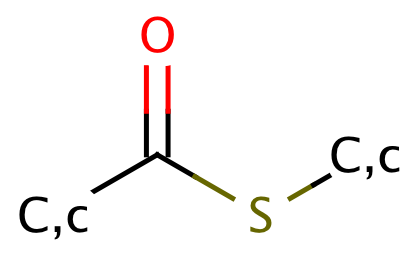
|
1 | 53 |
| thioic_acid |
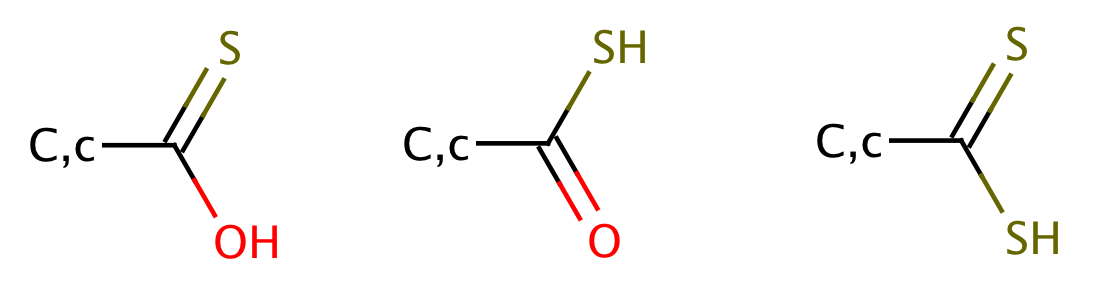
|
1 | 63 |
| thioketone |
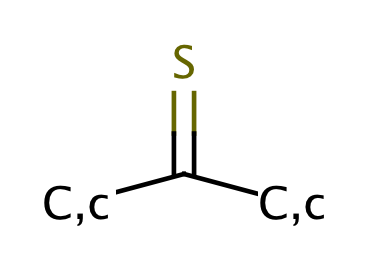
|
1 | 63 |
| thiol |
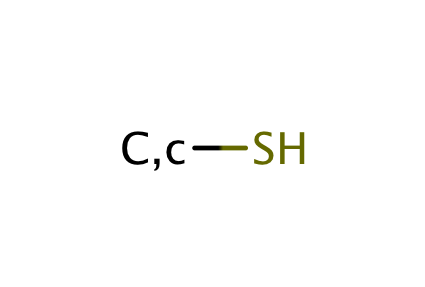
|
1 | 44 |
| thiophene |
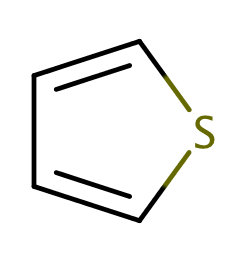
|
1 | 44 |
| toxoflavins |
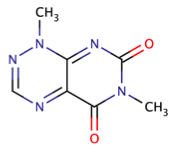
|
1 | 66 |
| triacyloxime |
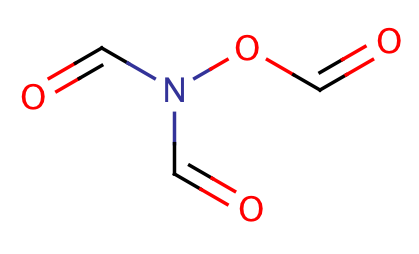
|
1 | 64 |
| triazenes |
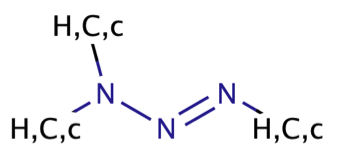
|
1 | 60, 66 |
| triflate |
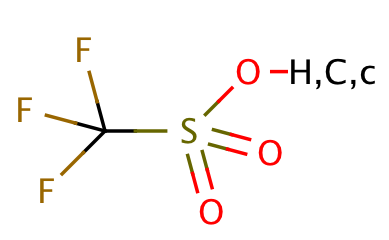
|
1 | 63, 64 |
| triphenyl |
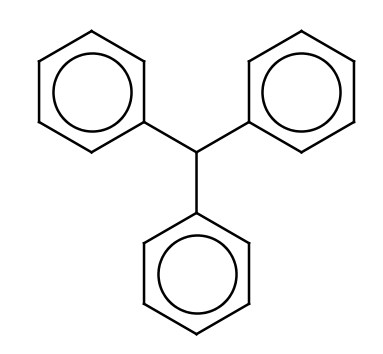
|
1 | 53 |
» Frequents Hitters according to Roche et al. [20].
Compounds which show up as hits in many different biological assays covering a wide range of targets, because of the activity of the compound is not specific for the target and/or the compound perturbs the assay or the detection method. Compounds which contains that kind of moieties are poor starting points for drug discovery programs and in general must be removed, Thus, the default value allowed for the substructures/compounds is set to 0
» Aggregators according to McGovern et al. [21].
Aggregators are nonspecific compounds susceptible to form submicrometer aggregates. It has been suggested that this aggregate species is responsible for the inhibition of many different enzymes. Compounds which contains that kind of moieties must be removed. Thus, the default value allowed for the substructures/compounds is set to 0
» Pan Assay Interference compoundS (PAINS). The PAINS structures are not listed here, please see Baell et al. publication Supporting Information Tables and Figures [23] and the dedicated page